Watch parts are not just something to leave to the professionals.
We are all guilty of sending our luxury watches off for repair, nodding along as the service advisor discusses the faulty sections, and secretly having no idea what they are saying.
If you are tired of not understanding how watches work, this article is for you. We will define all of the main sections of a timepiece, from the mechanism to the dial, as well as showing you a helpful diagram.
When you understand the science behind your watch, you will be better equipped to recognise problems, fix minor issues, and have a coherent conversation with the servicer.
Watch Parts Diagram
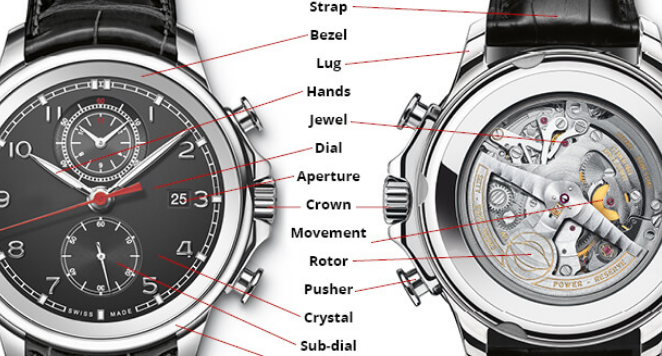
Before we begin to explain exactly how watches work, here is a useful diagram. It does not cover all watch parts names, but it shows us the most important features of a timepiece.
Inner Workings

The inner workings of a watch usually hide away under the dial. However, some watches feature windows that allow us to peak into the mechanism and see the following watch movement parts:
Movement/Caliber
The movement is the engine of the timepiece; it provides the power to get the other parts moving. It can be mechanical, quartz, or automatic.
Rotor
Automatic watches often feature a rotor. It swings back and forth when you move your wrist, which provides the energy to wind the mainspring.
Mainspring
This is a coiled metal spring that appears in mechanical watches. It is powered by either regular winding (mechanical watches) or wrist movement (automatic watches). The purpose of a mainspring is to power the wheels of the watch.
Escapement
This controls the power of the mainspring and ensures it is released slowly. The escapement is known for producing the classic ticking sound of a watch.
Balance Wheel & Balance Spring
The balance spring in your watch causes the balance wheel to move in an orderly way, which controls the speed of the wheels.
Jewel
Sometimes jewels are placed inside holes in the movement. They reduce friction which prevents the mechanism from deteriorating quickly.
Complications

Today’s watches often feature complications as they add to the uniqueness of a timepiece. There are many different types of complication, but here are a few that are currently popular:
Tourbillon
A tourbillon is a modified watch movement, where the escapement and balance wheel are placed inside a moving cage. This counteracts the effects of gravity on the watch’s accuracy.
Moonphase
The moonphase is popular among space fanatics. It displays the different phases of the moon either visually or with an indicator hand. You will usually see two moons in the middle of the dial and then a disc below the moons. An impressive 59-tooth wheel manoeuvres the disc.
Chronograph
A traditional watch complication, the chronograph is a combination between a display watch and a stopwatch. It consists of several displays which means chronographs tend to be more accurate than other watches.
Dial

The dial is slightly easier to understand as we get to see it in all its glory. In watch dials, we commonly see the following wrist watch parts:
Hands
The watch hands move around the dial to indicate the time. They come in many shapes and sizes, from triangular dauphine hands to sword hands.
Hour Marker
We use hour markers as a creative way of showing the time. Some popular types of hour marker include: Roman numerals, Arabic numerals, arrow-shaped, square-shaped, and batons.
Sundial
Subdials are smaller dials that are displayed on the main dial. You will often see chronograph and moonphase subdials.
Crystal
This is the glass that covers the dial to protect it from damage. It is commonly made of plastic, mineral, or sapphire and can be scratch resistant.
Case

You will also be familiar with the watch case. This is the material that surrounds the dial and is usually round, though it can also be square or rectangular. Here are some parts of a watch that we can identify on the case:
Crown
Placed on the side of the case, you can use the crown to alter the time displayed on the watch.
Bezel
This is the ring that surrounds the case and secures the crystal glass. Many timepieces feature rotating bezels, which means that watch enthusiasts can easily track time underwater.
Lugs
On the top and bottom of your watch case, you will find the lugs. The lugs keep the strap or bracelet fixed to the case.
Watch Band Parts

The watch band is what distinguishes wrist watches from pocket watches. There are two types of bands:
Metal Bracelet
This type is sophisticated and durable, but it is also heavier and can be more difficult to clean.
Strap
Straps come in a wide variety of materials such as leather, rubber, and nylon, and each material has its own benefits and drawbacks. Overall, most watch straps are comfortable and versatile but much less durable than metal.
Our Final Thoughts On Watch Parts
We hope this article has answered all your questions surrounding the composition of a timepiece. Here’s to hoping your next conversation at the watch repair shop goes smoothly now that you know all about how a watch works.
If all this talk about how watches function has made you want to purchase one, you’re in the right place. You may know Uniform Wares for our collection of premium Swiss-made watches for men and women. Why not see what’s on offer today? Browse our watches for sale.
